Industrial hemp of Hokkaido -the challenge towards a future-
EU hemp
1.History of deregulation
In the EU, hemp cultivation continued after World War II in Eastern European nations under the influence of the former Soviet Union (Poland, Hungary, Romania and so on), but in the major countries of Western Europe, such as Germany, the UK, the Netherlands and Austria, cultivation was temporarily prohibited after the war. The sole exception was France, where hemp was never restricted due to its historical cultivation for use in paper pulp.
Reconsideration of hemp spread in the 1990s, in a background of environmental and health issues. Cultivation bans were lifted, albeit only for industrial hemp with an effective THC content of less than 0.3%, in 1993 in the UK, 1994 in the Netherlands, and 1996 in Germany and Austria. A subsidies scheme under the EU's Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) came in as a result of cultivation bans being lifted. Hemp is currently located in the Flax and Hemp entry in the EU's agricultural regulations. This entry is a subsidies based on the European Common Market Organization (CMO)'s Enforcement Convention (EC) No 1673/2000. The convention was enacted to unify the laws of all member nations in the EU legal system, and has a direct effect in those countries, taking precedence over all national laws.
Many of the details of this subsidies scheme have changed since EEC convention No. 1308/70 was issued in 1970 until today. For example, since 2001 the THC standard has been severely cut from 0.3% to 0.2%, and a list of breeds and THC measurement process documents have been issued. In 2008 the subsidy under this system was 90 Euros per 1 ton bundle of hemp straw.
2.Cultivation conditions
・- EU regulations restrict cultivated breeds to those with less than 0.2%
THC content.
- No. A-63 out of the 87 types of agricultural varieties in the EU Common
Breeds Catalog is "Hemp- Cannabis sativa", with 52 breeds listed.
(As of the end of May 2015)
- Farmers in the EU obtain seeds from companies, designated by the French government, that specialize in hemp, and from some agricultural experiment stations that possess hemp seeds.
- Farmers do not require a special license for growing hemp.
- If a breed has less than 0.2% THC, not only the seeds and stalks (fibers and reeds), but also the leaves and spikes can legally be made into products such as beer, herbal tea, essential oils, perfume and medical materials.
(It is illegal in Japan to use the leaves and spikes of any breeds)
3.Current market
Market size(2012) 7 - 8 billion yen
Cultivation area(2016) 33,000 ha
4.Usage applications
| Material | Applications |
| Hemp Fiber | Pulp and paper 55%、Insulation 26%、Automotive composite(14%、Technical textiles 3%, Other |
| Shivies/Hards | Animal bedding(Horses)45%、Animal bedding(Other than horses)17%、Construction15%、Garden mulch 19%,Other(Fungi, incineration) |
| Hemp seed | Feed 44%、Food 43% for Oil(Food) 13%、for Oil(Feed, Cometics) |
| Flower | Essential oil, raw materials for medical use |
出典:Michael Carus, Stefan Karst, Alexandre Kauffmann, John Hobson and Sylvestre
Bertucelli, The European Hemp Industry: Cultivation, processing and applications
for fibres, shivs and seeds, EIHA,(2015)
Canada hemp, Food and Medical use
1. History of deregulation
In Canada, the production of hemp was prohibited by the 1938 Opium and Narcotic Drug Act. Interest in hemp as a new business grew in the 1990s, and research inquiries were held from 1994-1998. As a result, Canada's Ministry of Health decided to allow its use in agricultural and industrial fields under prescribed restrictions. This established the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act (CDSA), enacted in 1997, and the 1998 Industrial Hemp Regulations, which legalized hemp cultivation. In this regulations, the definition of industrial hemp is specified as follows.
"Industrial hemp means the plants and plant parts of the genera Cannabis,
the leaves and flowering heads of which do not contain more than 0.3% THC
w/w, and includes the derivatives of such plants and plant parts. It also
includes the derivatives of non-viable cannabis seed. It does not include
plant parts of the genera Cannabis that consist of non-viable cannabis
seed, other than its derivatives, or of mature cannabis stalks that do
not include leaves, flowers, seeds or branches, or of fibre derived from
those stalks."
If the leaves and flowes have less than 0.3% THC, the entire plant can
be used, and seeds capable of germination are included as industrial hemp.
Seeds, stalks and fibers that are incapable of germination have not been
subject to regulation since the acts were enacted, and are not included
in the definition of industrial hemp. Canada's regulations are characterized
by the existence of 9 types of permit, for cultivation, import, export,
processing, delivery, possession, breeding, analysis, and sample tests,
managing everything from production to import and export. Permit applicants
have to fulfill preexisting conditions, and must also receive a police
security inspection, an investigation of THC levels in leaves and derived
substances in accordance with standards defined by the Canadian Ministry
of Health, carried out by a qualified inspection agency.
2.Cultivation conditions
- Limited to 44 breeds (2015) with under 0.3% THC.
- A permit from the (state) Ministry of Health is required.
There are 9 types of permit, for cultivation, import, export, processing, delivery, possession, breeding, analysis, and sample tests.
- Farmers purchase seeds from 3 domestic seed companies in Canada that deal in hemp.
- An annual inspection from an agency with a THC inspection permit is also required after cultivation.
3.Current market
<Industrial hemp section>
Market size(2014): About 5.7 Billion yen(Export)
Cultivation area:26982 ha(2013)、43912 ha(2014)、50600 ha(2015)
Licence:768 people(2014)
<Medical marijuana section>
BC, Matket size(2011):$6 billion
Number of patients :15000~20000 people
※Canada has legalized medical marijuana since 2003 as well.
4.Usage applications
Most use it for edible hemp.
Resource:Daniel Kruse, New Data on Hemp Food Market and THC Limits for
Food and Feed, EIHA 12th conference 2015
"B.C.’s medicinal marijuana business growing" Business In Vancouver,
Jul 3, 2012
American hemp
1.History of deregulation
It is known that founding father of America George Washington grew hemp, and that the Declaration of Independence was written on hemp paper. In the 1800s, the country's fabrics and paper were mainly made from hemp, but substantial cultivation was made impossible by the Marijuana Tax Act of 1937, enacted after Prohibition was repealed.
The hemp ban was temporarily lifted during World War II, as it was necessary for military uniforms, ropes on battleships, cords for parachutes and so on, but after the war it was no longer grown. America proposed regulation of "marijuana" in the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961, and from its adoption by the UN, became a leader of a campaign to eradicate marijuana around the world. However, smoking marijuana spread among young people in the hippie and anti war movements of the 1970s as a countercultural fashion. People using marijuana to self medicate for AIDS, glaucoma, the pain of cancer and so on gradually increased. A separation arose between the legislation and the reality.
The state of California legalized marijuana use for medicinal purposes in a 1996 local referendum, and the number of states that followed suit increased to a current total of 23, plus Washington DC. Furthermore, the states of Washington and Colorado legalized recreational marijuana as a result of local referenda in 2013. On the other hand, several states have begun to cultivate hemp for industrial purposes since the approval of the Industrial Hemp Farming Act of 2014. On the topic of opposing views on medical and recreational marijuana at the federal and state levels, a bill is being proposed to gain consistency between state governments and Congress.
2.Cultivation conditions
Farming:Feb.2014 7606 of act Pass
May.2014 H.R.4660 Pass
Medical:The patient cultivates in-house. The number is 3 to 18 and it is
stipulated by state law.If a patient can not cultivate, a care giver can
substitute
3.Current market
<Farming:Fiber and Seed type varities>
Total U.S. Hemp-Based product sales :$ 688 Million
Cultivation area : 3905 ha(2016)
Ex.Kentucky state: 13 ha(2014), 5179 ha (2017)
<Medical : Drug type varities>
Total U.S. Market size:$ 2.7 billion(2014)
$ 13 billion (Estimate 2020)
29 states legalized + Wasinton D.C.
4.Usage applications
| Section | Applications |
| Industrial | Clothing, strings and accessories, health food, cosmetics, paper, building materials etc. |
| Medical | In the case of Oregon, 92% of serious pain, 25% of persistent convulsions, 13% of serious nausea, 5% of cancer, 2% of seizures, 1% of cachexia, 1% of cachexia, 1% of endometriosis, 1% of AIDS, Alzheimer The excitement of less than 1%. Approximately 20% of patients, in particular morphine analgesics, do not fit constitutively, are present and are saved by the marijuana analgesic effect for those. |
Resource:Anndre Hermann USA and Canadian Hemp Update Production, Regulation
and Reality EIHA 12th conference 2015.
The State of Legal Marijuana Markets 3rd Edition Arec View Market Reserch
2015.
China hemp
1.History
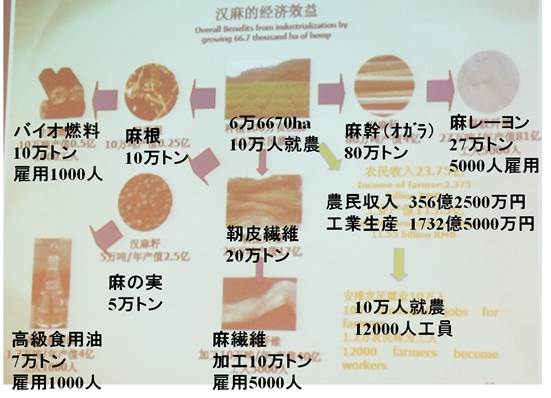
Hemp was a traditional crop in China, and numerous studies on its breeding and cultivation were made in the 1950s. However, production decreased by more than 90% after the 50s, when policies prohibiting hemp cultivation were enacted globally. China's hemp cultivation is distributed among Heilongjiang, Jilan, Liaoning, Hebei, Shanxi, Shandong, Anhui, Henan, and Gansu. 20-30,000 tons are produced annually, still the largest amount grown worldwide. In China, hemp is called by different names in the northeast, Shanxi, Anhui, Gansu, and Yunnan respectively.
Since 2007, the Chinese military's Hemp Material Research Center and the
Youngor Group, No 1 in the clothing world, have financed the establishment
of the Hemp Industry Investment Holdings Limited Company, with investments
of 2 hundred million yuan (roughly 30 billion yen). A new, state of the
art spinning mill was established in Yunnan in 2009, which has produced
5000 tons of hemp fiber a year since 2011.
There are several reasons why the Chinese state is committed to hemp. Reducing the economic disparity between coastal and inland regions, hemp can be grown as a crop in mountainous areas, wilderness, and salty, barren soil, as a means of solving the desertification, food scarcity, oil scarcity, lack of morale, drying up of water, and agricultural problems that the Chinese state faces, with the aim of strengthening China's industrial competitiveness as a result.
2.Cultivation conditions
According to the People's Republic of China state recommended standard
"GB/T16984-2008 Raw Hemp",varities names have been given definitions
based on THC content since 2008.
Low toxicity industrial hemp varities: under 0.3% THC
Non toxic hemp varities: under 0.1% THC
However, given there is a long history of hemp cultivation, actual growth
is not managed to such a strict degree. An exception is Yunnan, where provincial
regulations determine a standard of less than 0.3% THC.
3.Current market
For Fiber; 20000 ha、For Seeds; 60000 ha (2016)
Chinese military's Hemp Material Research Center
4.Usage applications
| Material | Application |
| Fibers | Spining yarn, Cloth etc. |
| Shivies | Firewood for burning (wood is a valuable item in China because its forest ratio is only 14%) |
| Seeds | Feed and edible for export |